Congrats to Shurui and others!
Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Lu, Y., Yuan, S., Wang, L., Xu, L., Yi, K., & Jia, X. (2025). Plant STOP1 family: A helmsman in the soil multiple stress adaptation. Plant and Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-025-07807-7
Title: Plant STOP1 family: a helmsman in the soil multiple stress adaptation
Authors: Shurui Zhang, Yanlin Wang, Yao Lu, Shuai Yuan, Long Wang, Lei Xu, Keke Yi, Xianqing Jia
Abstract: Abiotic stresses significantly reduce crop yields worldwide, with common stressors including drought, flooding, hypoxia, nutrient deficiency, as well as proton and heavy metal toxicity. STOP1 (Sensitive to Proton Toxicity 1) and its homologs were initially found to function as key transcription factors in regulating plant tolerance to both low pH and aluminum toxicity. Recently, increasing evidence has revealed additional roles of STOP1 in coping with multiple environmental stresses, including enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus uptake efficiency, remodeling root architecture, boosting hypoxia tolerance via physiological regulation, negatively regulating drought resistance by modulating water loss, and increasing salt tolerance under low potassium conditions. These findings highlight the significant potential of STOP1 as a key target for improving crop tolerance to diverse environmental stresses. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the central roles of STOP1 and its underlying mechanisms in regulating multiple stress responses. We also propose further work that might help uncover the roles of STOP1 in soil multiple stress adaptation in plants and its application in crop improvement. A deeper understanding of the pleiotropic role of the STOP1 family in plant stress response will help us to systematically understand the resistance mechanism of crops and improve crop performance.
News:
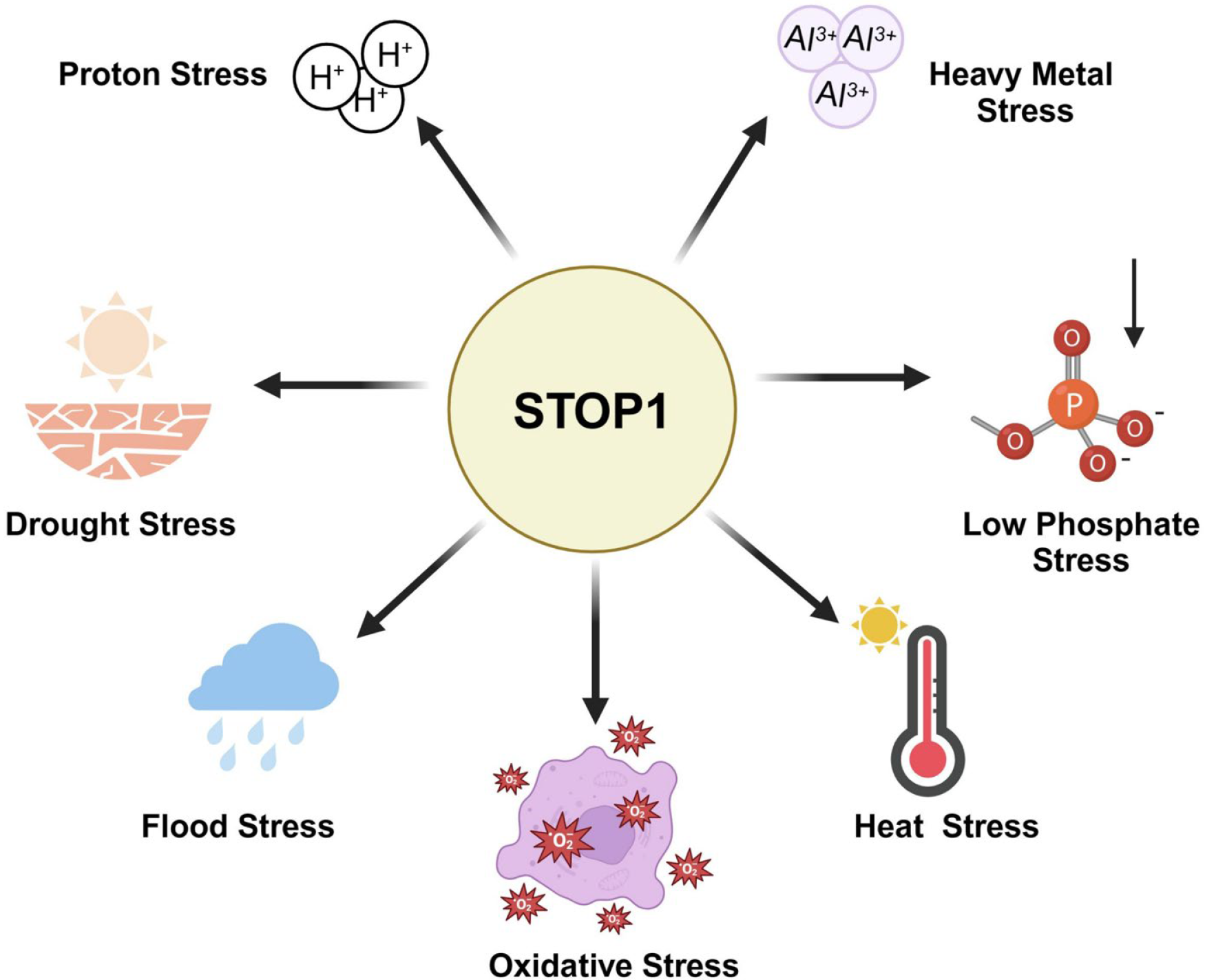
Overview of STOP1 family in regulating plant multi-stress response
The STOP1 gene regulates responses to multiple environmental stresses, including proton stress, heavy metal stress (particularly aluminum toxicity), low phosphate stress, heat stress, oxidative stress, flood stress, and drought stress. By activating different downstream response mechanisms, STOP1 helps plants adjust their growth and survival under adverse conditions.